购物车
- 全部删除
 您的购物车当前为空
您的购物车当前为空

Sangivamycin (NSC-65346) 是蛋白激酶 C (PKC) 的有效抑制剂 (Ki = 10 μM)。 Sangivamycin 对多种人类癌症细胞具有抗增殖活性。

为众多的药物研发团队赋能,
让新药发现更简单!
Sangivamycin (NSC-65346) 是蛋白激酶 C (PKC) 的有效抑制剂 (Ki = 10 μM)。 Sangivamycin 对多种人类癌症细胞具有抗增殖活性。
| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 mg | ¥ 1,070 | 现货 | |
| 5 mg | ¥ 2,820 | 现货 | |
| 10 mg | ¥ 4,130 | 现货 | |
| 25 mg | ¥ 6,470 | 现货 | |
| 50 mg | ¥ 8,720 | 现货 | |
| 100 mg | ¥ 11,700 | 现货 | |
| 1 mL x 10 mM (in DMSO) | ¥ 1,890 | 现货 |
| 产品描述 | Sangivamycin (NSC-65346) is an effective inhibitor of protein kinase C (PKC, Ki = 10 μM). Sangivamycin exhibits antiproliferative activity against a variety of human cancers. |
| 靶点活性 | PKC:10 μM(Ki) |
| 体外活性 | Sangivamycin(0.3 μM;0-72小时)对MCF7/ADR细胞展现几乎最大的细胞杀伤效果,或对MCF7/WT细胞显示出细胞静止效应。Sangivamycin在MCF7/ADR细胞中激活caspases。当MCF7/ADR细胞暴露于Sangivamycin(0.3 μM)时,48小时内检测到大量lamin A裂解成28-kDa片段。Sangivamycin在药物敏感的MCF7/野生型(WT)细胞中具有不同的抗肿瘤效应,引起生长停滞,在多药耐药的MCF7/阿霉素耐药(ADR)人乳腺癌细胞中引起大量凋亡性细胞死亡[2]。 |
| 别名 | 桑霉素, NSC 65346, BA-90912 |
| 分子量 | 309.28 |
| 分子式 | C12H15N5O5 |
| CAS No. | 18417-89-5 |
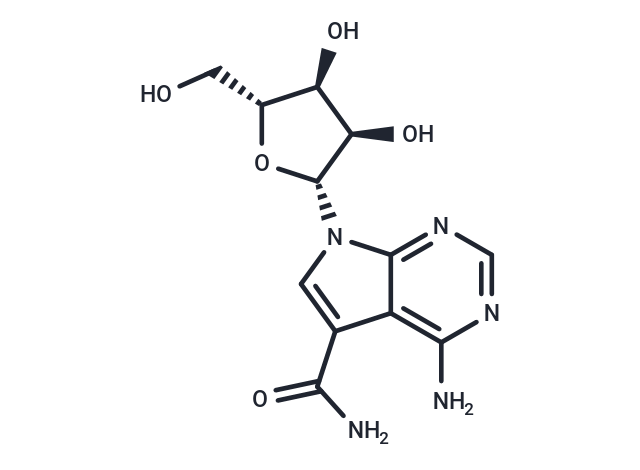
| Smiles | NC(=O)c1cn([C@@H]2O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O)[C@H]2O)c2ncnc(N)c12 |
| 密度 | 1.3120 g/cm3 (Estimated) |
| 存储 | Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 溶解度信息 | DMSO: 95 mg/mL (307.17 mM), Sonication is recommended. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
溶液配制表 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
DMSO
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
以上为“体内实验配液计算器”的使用方法举例,并不是具体某个化合物的推荐配制方式,请根据您的实验动物和给药方式选择适当的溶解方案。
评论内容