Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year
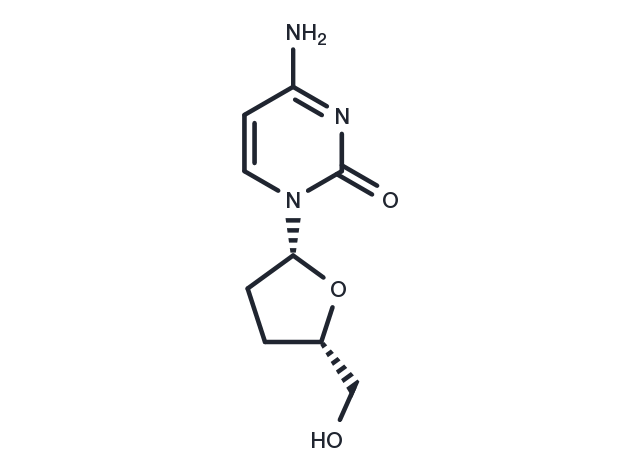
Zalcitabine (Dideoxycytidine) 是一种核苷类似物逆转录酶抑制剂,用于HIV 感染相关研究。
| 规格 | 价格/CNY | 货期 | 数量 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 25 mg | ¥ 259 | 现货 | ||
| 50 mg | ¥ 349 | 现货 | ||
| 100 mg | ¥ 547 | 现货 | ||
| 200 mg | ¥ 783 | 现货 | ||
| 500 mg | ¥ 1,330 | 现货 | ||
| 1 mL * 10 mM (in DMSO) | ¥ 391 | 现货 | ||
| 产品描述 | Zalcitabine (Dideoxycytidine)(Dideoxycytidine;ddC; 2', 3'-Dideoxycytidine) is a nucleoside analog reverse transcriptase inhibitor (NRTI); At low concentrations, It can potently inhibit HIV replication by binding to reverse transcriptase terminated synthesis of viral DNA chain. |
| 体外活性 | Zalcitabine是一种双脱氧核苷类抗逆转录病毒药物,在未感染细胞和感染艾滋病毒的细胞中都会磷酸化成活性代谢物 2',3'-双脱氧胞苷 5'-三磷酸酯(ddCTP)。在治疗浓度下,ddCTP 可通过抑制逆转录酶和终止前病毒 DNA 链的延伸来抑制 HIV 的复制[1]。Zalcitabine对 CHO/hOAT1 细胞摄取 [3H]-PAH 具有抑制作用,IC50 值为 1.23 mM。此外,随着 CHO/hOAT1 细胞中 hOATI 活性的增强,细胞对Zalcitabine的吸收增加了三倍[2]。 |
| 别名 | Dideoxycytidine, ddC, 扎西他滨, NSC 606170, Ro 24-2027/000, 2',3'-Dideoxycytidine |
| 分子量 | 211.22 |
| 分子式 | C9H13N3O3 |
| CAS No. | 7481-89-2 |
Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year
DMSO: 16.67 mg/mL (78.92 mM)
| 可选溶剂 | 浓度 体积 质量 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 25 mg |
| DMSO | 1 mM | 4.7344 mL | 23.672 mL | 47.344 mL | 118.36 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.9469 mL | 4.7344 mL | 9.4688 mL | 23.672 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.4734 mL | 2.3672 mL | 4.7344 mL | 11.836 mL | |
| 20 mM | 0.2367 mL | 1.1836 mL | 2.3672 mL | 5.918 mL | |
| 50 mM | 0.0947 mL | 0.4734 mL | 0.9469 mL | 2.3672 mL |
对于不同动物的给药剂量换算,您也可以参考 更多...
请在以下方框中输入您的动物实验信息后点击计算,可以得到母液配置方法和体内配方的制备方法: 比如您的给药剂量是10 mg/kg,每只动物体重20 g,给药体积100 μL,一共给药动物10 只,您使用的配方为5% DMSO+30% PEG300+5% Tween 80+60% ddH2O。那么您的工作液浓度为2 mg/mL。
母液配置方法:2 mg 药物溶于 50 μL DMSO (母液浓度为 40 mg/mL), 如您需要配置的浓度超过该产品的溶解度,请先与我们联系。
体内配方的制备方法:取 50 μL DMSO 主液,加入 300 μL PEG300, 混匀澄清,再加 50 μL Tween 80,混匀澄清,再加 600 μL ddH2O, 混匀澄清。
您可能有的问题的答案可以在抑制剂处理说明中找到,包括如何准备库存溶液,如何存储产品,以及基于细胞的分析和动物实验需要特别注意的问题。
Zalcitabine 7481-89-2 Microbiology/Virology Proteases/Proteasome Reverse Transcriptase HIV Protease Dideoxycytidine NSC606170 NSC-606170 inhibit ddC Human immunodeficiency virus 扎西他滨 NSC 606170 HIV Ro 24-2027/000 2',3'-Dideoxycytidine Inhibitor inhibitor
