Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year
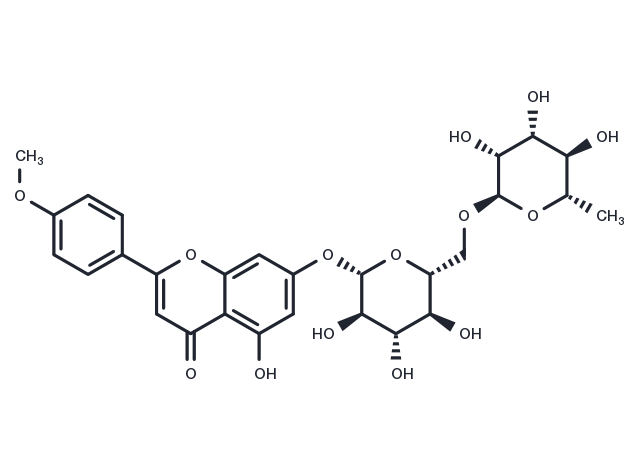
Linarin (Acacetin-7-O-rutinoside) 是一种选择性的乙酰胆碱酯酶 (AChE) 抑制剂,从薄荷花提取物中分离得到。
| 规格 | 价格/CNY | 货期 | 数量 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 mg | ¥ 218 | 现货 | ||
| 5 mg | ¥ 497 | 现货 | ||
| 10 mg | ¥ 828 | 现货 | ||
| 25 mg | ¥ 1,450 | 现货 | ||
| 50 mg | ¥ 2,290 | 现货 | ||
| 100 mg | ¥ 3,430 | 现货 | ||
| 1 mL * 10 mM (in DMSO) | ¥ 648 | 现货 | ||
| 产品描述 | 1. Linarin (Acacetin-7-O-rutinoside) (acacetin-7-O-β-d-rutinoside) shows selective dose dependent inhibitory effect on acetylcholinesterase. 2. Linarin alleviates GalN/LPS-induced liver injury by suppressing TNF-α-mediated apoptotic pathways. 3. Linarin prevents A beta-induced neurotoxicity through the activation of PI3K/Akt, which subsequently inhibits GSK-3b and up-regulates Bcl-2. 4. The piperine significantly enhanced the oral absorption of Linarin in rats by inhibiting P-glycoprotein mediated cellular efflux during the intestinal absorption and likely simultaneously by inhibiting the metabolism of Linarin. |
| 别名 | Buddleoflavonoloside, Buddleoside, Acacetin-7-O-rutinoside, Acaciin, Linarine, 蒙花苷 |
| 分子量 | 592.55 |
| 分子式 | C28H32O14 |
| CAS No. | 480-36-4 |
Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year
Pyridine, Methanol, etc.: Soluble
DMSO: 91 mg/mL(153.6 mM)
Ethanol: Soluble
| 可选溶剂 | 浓度 体积 质量 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 25 mg |
| DMSO | 1 mM | 1.6876 mL | 8.4381 mL | 16.8762 mL | 42.1905 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.3375 mL | 1.6876 mL | 3.3752 mL | 8.4381 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.1688 mL | 0.8438 mL | 1.6876 mL | 4.2191 mL | |
| 20 mM | 0.0844 mL | 0.4219 mL | 0.8438 mL | 2.1095 mL | |
| 50 mM | 0.0338 mL | 0.1688 mL | 0.3375 mL | 0.8438 mL | |
| 100 mM | 0.0169 mL | 0.0844 mL | 0.1688 mL | 0.4219 mL |
| 中药材名称 | 中药材拉丁名 | 性 | 味 | 归经 |
| 金荞麦 | Fagopyrum dibotrys(D.Don)Hara | 凉 | 微辛, 涩 | 肺 |
| 中成药名称 | 处方组成 | 主治疾病 | 中成药类型 |
| 急支颗粒 | 鱼腥草,金荞麦,四季青,麻黄,紫菀,前胡,枳壳,甘草 | 口服,一次4克,一日3~4次。 | 化痰、止咳、平喘药 |
| 清咳平喘颗粒 | 生石膏,川贝母,金荞麦,鱼腥草,麻黄(蜜炙),苦杏仁(炒),矮地茶,枇杷叶,紫苏子(炒),甘草(炙) | 开水冲泡,温服,一次10g,一日3次。 | 温经理气活血药 |
| 双金胃疡胶囊 | 雪胆,金荞麦,大血藤,紫珠,麻布袋,延胡索,仙鹤草,白及,凤凰衣,土木香,核桃仁 | 口服,一次3粒,一日3次。 | 扶正药 |
| 喘络通胶囊 | 鸡根,金荞麦,人参,紫河车,蛤蚧,地龙,蟾酥,浙贝母,麻黄,苦杏仁,甘草 | 口服。一次3~4粒,一日3次;饭后温开水送服,儿童酌减。 | 化痰、止咳、平喘药 |
| 金刺参九正合剂 | 刺梨果(鲜),苦参,金荞麦 | 口服,一次20~40ml,一日2次;或遵医嘱。 | 扶正药 |
| 红金消结片 | 金荞麦,大红袍,柴胡,黑蚂蚁,五香血藤,三七,香附 | 口服,一次4片,一日3次。 | 祛瘀药 |
| 双金胃肠胶囊 | 雪胆,金荞麦,大血藤,紫珠,麻布袋,延胡索,仙鹤草,白及,凤凰衣,土木香,核桃仁 | 口服,一次3粒,一日3次。 | 扶正药 |
| 红金消结浓缩丸 | 三七,八角莲,鼠妇虫,黑蚂蚁,五香血藤,鸡矢藤,大红袍,金荞麦,柴胡 | 口服,一次10丸,一日三次。 | 祛瘀药 |
| 神农药酒 | 寻骨风,川芎,丹参,当归,防风,杜仲,五加皮,老鹳草,大血藤,木香,络石藤,红花,牛藤,路路通,柴胡,制草乌,射干,独活,鸡血藤,苍术,爬岩香,威灵仙,徐长卿,钩藤,老虎蔸,三百棒,伸筋草,三七,莲逢草,八角莲,八棱麻,香茶荣,虎杖,金荞麦,拳参,山姜,蜘蛛抱蛋,菊叶三七,木梳,雄黄连,搜山虎,八角枫,算盘子根 | 口服,一次25ml,一日2次。 | 祛风药 |
| 金花止咳颗粒 | 鱼腥草,金荞麦 | 一次5g,一日2次。 | 化痰、止咳、平喘药 |
| 金荞麦咀嚼片 | 金荞麦 | 咀嚼服用。一次4~5片,一日3次。 | 化痰、止咳、平喘药 |
| 金花明目丸 | 熟地黄,盐菟丝子,枸杞子,五味子,白芍,黄精,黄芪,党参,川芎,菊花,炒决明子,车前子(炒),密蒙花,炒鸡内金,金荞麦,升麻,山楂 | 饭后口服,每次4g,每日3次。 | 扶正药 |
| 金荞麦胶囊 | 金荞麦 | 口服。一次4~5粒,一日3次。 | 化痰、止咳、平喘药 |
| 乌金活血止痛片 | 赤芍,倒提壶(制),金荞麦 | 口服,一次1~2片,一1~日2次。一日最大用量不超过4片。体质虚弱者可用蜂蜜,大枣煎汤送服。 | 祛瘀药 |
| 妇平胶囊 | 金荞麦,紫花地丁,莪术,败酱草,杠板归,大血藤,一枝黄花 | 口服,一次2粒,一日3次。 | 清热药 |
| 金荞麦片 | 金荞麦 | N/A | 解表药 |
| 九龙解毒胶囊 | 盘龙参,穿心莲,轮环藤根,一支箭,金荞麦,山枝茶 | 口服。一次1-2粒,一日4次;重症加倍。 | 清热药 |
| 急支糖浆 | 鱼腥草,金荞麦,四季青,麻黄,紫菀,前胡,枳壳,甘草 | 口服一 次20?30ml,一日3?4次;儿童周岁以内一次5ml,一至三岁一次7ml,三至七岁一次10ml,七岁以上一次15ml,一日3?4次 。 | 化痰、止咳、平喘药 |
| 金胃泰胶囊 | 大红袍,鸡矢腾,管仲,金荞麦,黄连,砂仁,延胡索,木香 | 口服,一次3粒,一日3次。 | 扶正药 |
| 乌金活血止痛胶囊 | 倒提壶,赤芍,金荞麦 | 口服。每次1-2粒,每日2次,一日最大剂量不超过4粒。 | 祛瘀药 |
对于不同动物的给药剂量换算,您也可以参考 更多...
请在以下方框中输入您的动物实验信息后点击计算,可以得到母液配置方法和体内配方的制备方法: 比如您的给药剂量是10 mg/kg,每只动物体重20 g,给药体积100 μL,一共给药动物10 只,您使用的配方为5% DMSO+30% PEG300+5% Tween 80+60% ddH2O。那么您的工作液浓度为2 mg/mL。
母液配置方法:2 mg 药物溶于 50 μL DMSO (母液浓度为 40 mg/mL), 如您需要配置的浓度超过该产品的溶解度,请先与我们联系。
体内配方的制备方法:取 50 μL DMSO 主液,加入 300 μL PEG300, 混匀澄清,再加 50 μL Tween 80,混匀澄清,再加 600 μL ddH2O, 混匀澄清。
您可能有的问题的答案可以在抑制剂处理说明中找到,包括如何准备库存溶液,如何存储产品,以及基于细胞的分析和动物实验需要特别注意的问题。
Linarin 480-36-4 Apoptosis Neuroscience TNF AChE arvensis Buddleoflavonoloside Buddleoside Inhibitor acetylcholinesterase inhibit Acacetin-7-O-rutinoside Mentha Acaciin Linarine Cholinesterase (ChE) 蒙花苷 inhibitor
