Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year
Fluxametamide 是广谱杀虫剂,是 GABA-和谷氨酸门控氯离子通道拮抗剂,对 M. domestica 中 GABACl 和 GluCl 的IC50值分别为 1.95 和 225 nM。
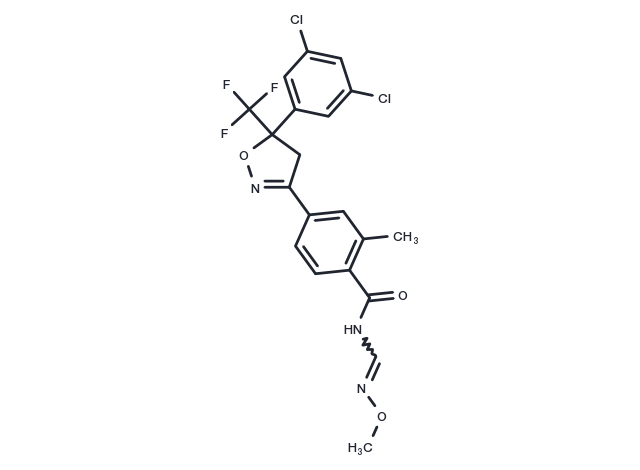
| 规格 | 价格/CNY | 货期 | 数量 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 mg | ¥ 315 | 现货 | ||
| 5 mg | ¥ 747 | 现货 | ||
| 10 mg | ¥ 1,230 | 现货 | ||
| 25 mg | ¥ 2,660 | 现货 | ||
| 50 mg | ¥ 4,290 | 现货 | ||
| 100 mg | ¥ 6,150 | 现货 | ||
| 1 mL * 10 mM (in DMSO) | ¥ 822 | 现货 | ||
| 产品描述 | Fluxametamide is a novel isoxazoline insecticide that acts via distinctive antagonism of insect ligand-gated chloride channels, acts as an antagonist of GABA- and glutamate-gated chloride channels(IC50 of 1.95 nM and 225 nM for M. domestica GABACls and GluCls). |
| 靶点活性 | GABACls (M. domestica):1.95 nM , GluCls (M. domestica):225 nM |
| 体外活性 | Fluxametamide在野生型L. striatellus GABACls上抑制GABA反应,IC50值为1.40(0.57-3.29)nM;在A2′N突变体GABACls上,IC50值为3.51(2.17-5.69)nM。此外,Fluxametamide在10 μM浓度下对大鼠GABACls的GABA(EC50)诱导电流几乎不表现抑制作用,且在测试浓度下不抑制人类α1 GlyCls的甘氨酸(EC50)诱导电流。Fluxametamide是一种GABA和谷氨酸门控氯离子通道的拮抗剂,其对M. domesticaGABACls和GluCls 由GABA和谷氨酸诱导的电流表现出剂量依赖性抑制,IC50值分别为1.95(1.18-3.21)nM和225(137-372)nM,并具有强大的拮抗作用,对 T. urticae GABACls的IC50为0.219(0.127-0.381)nM。 |
| 体内活性 | Fluxametamide 通过与现有拮抗剂不同的位点结合,独特地拮抗节肢动物的GABACls。与其对节肢动物LGCCs的显著作用相反,fluxametamide 对大鼠GABACls和人类甘氨酸门控氯离子通道的拮抗活性几乎可以忽略,这表明fluxametamide 对节肢动物相比哺乳动物具有高度的靶点选择性。总的来说,fluxametamide 是一种新型的LGCC拮抗剂杀虫剂,在靶点层面对哺乳动物具有极好的安全性。 |
| 别名 | 4-[5-(3,5-二氯苯基)-4,5-二氢-5-(三氟甲基)-3- 异恶唑基]-N-[(甲氧基氨基)亚甲基]-2-甲基苯 甲酰胺 |
| 分子量 | 474.26 |
| 分子式 | C20H16Cl2F3N3O3 |
| CAS No. | 928783-29-3 |
Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year
DMSO: 125 mg/mL (263.57 mM), Sonication is recommended.
| 可选溶剂 | 浓度 体积 质量 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 25 mg |
| DMSO | 1 mM | 2.1085 mL | 10.5427 mL | 21.0855 mL | 52.7137 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.4217 mL | 2.1085 mL | 4.2171 mL | 10.5427 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.2109 mL | 1.0543 mL | 2.1085 mL | 5.2714 mL | |
| 20 mM | 0.1054 mL | 0.5271 mL | 1.0543 mL | 2.6357 mL | |
| 50 mM | 0.0422 mL | 0.2109 mL | 0.4217 mL | 1.0543 mL | |
| 100 mM | 0.0211 mL | 0.1054 mL | 0.2109 mL | 0.5271 mL |
对于不同动物的给药剂量换算,您也可以参考 更多...
请在以下方框中输入您的动物实验信息后点击计算,可以得到母液配置方法和体内配方的制备方法: 比如您的给药剂量是10 mg/kg,每只动物体重20 g,给药体积100 μL,一共给药动物10 只,您使用的配方为5% DMSO+30% PEG300+5% Tween 80+60% ddH2O。那么您的工作液浓度为2 mg/mL。
母液配置方法:2 mg 药物溶于 50 μL DMSO (母液浓度为 40 mg/mL), 如您需要配置的浓度超过该产品的溶解度,请先与我们联系。
体内配方的制备方法:取 50 μL DMSO 主液,加入 300 μL PEG300, 混匀澄清,再加 50 μL Tween 80,混匀澄清,再加 600 μL ddH2O, 混匀澄清。
您可能有的问题的答案可以在抑制剂处理说明中找到,包括如何准备库存溶液,如何存储产品,以及基于细胞的分析和动物实验需要特别注意的问题。
Fluxametamide 928783-29-3 Membrane transporter/Ion channel Neuroscience GABA Receptor inhibit Inhibitor γ-Aminobutyric acid Receptor Gamma-aminobutyric acid Receptor 4-[5-(3,5-二氯苯基)-4,5-二氢-5-(三氟甲基)-3- 异恶唑基]-N-[(甲氧基氨基)亚甲基]-2-甲基苯 甲酰胺 inhibitor
