Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year
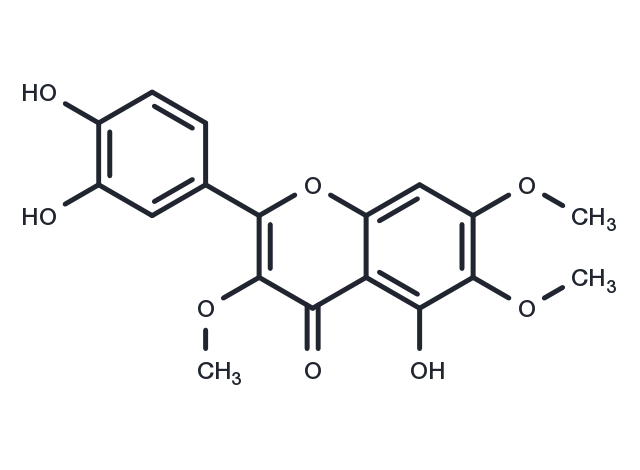
Chrysosplenol D 属于甲氧基黄酮类化合物,可诱导 ERK1/2 介导的三阴性人乳腺癌细胞凋亡。它还显示出抗炎和中等抗锥虫活性。
| 规格 | 价格/CNY | 货期 | 数量 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 mg | ¥ 996 | 现货 | ||
| 5 mg | ¥ 2,530 | 现货 | ||
| 10 mg | ¥ 3,970 | 现货 | ||
| 25 mg | ¥ 6,360 | 现货 | ||
| 50 mg | ¥ 8,690 | 现货 | ||
| 1 mL * 10 mM (in DMSO) | ¥ 2,590 | 现货 | ||
| 产品描述 | Chrysosplenol D, an efflux pump inhibitor that can potentiate the activity of commercially important antibiotics and antimalarials. |
| 靶点活性 | Viability:11.6 µM(MDA-MB-231 TNBC cells) |
| 体外活性 | Trace amounts of the antimalarial sesquiterpene lactone artemisinin may account for the activity of the n-hexane fraction but only the methoxylated flavonoids artemetin, chrysoplenetin, chrysosplenol-D and cirsilineol can account for the activity of the chloroform extract. These purified flavonoids were found to have IC50 values at 2.4 - 6.5 x 10(-5)M against P. falciparum in vitro compared with an IC50 value of about 3 x 10(-8)M for purified artimisinin[1] |
| 别名 | 猫眼草酚D |
| 分子量 | 360.31 |
| 分子式 | C18H16O8 |
| CAS No. | 14965-20-9 |
Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year
DMSO: 55 mg/mL (152.65 mM)
| 可选溶剂 | 浓度 体积 质量 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 25 mg |
| DMSO | 1 mM | 2.7754 mL | 13.8769 mL | 27.7539 mL | 69.3847 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.5551 mL | 2.7754 mL | 5.5508 mL | 13.8769 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.2775 mL | 1.3877 mL | 2.7754 mL | 6.9385 mL | |
| 20 mM | 0.1388 mL | 0.6938 mL | 1.3877 mL | 3.4692 mL | |
| 50 mM | 0.0555 mL | 0.2775 mL | 0.5551 mL | 1.3877 mL | |
| 100 mM | 0.0278 mL | 0.1388 mL | 0.2775 mL | 0.6938 mL |
| 中药材名称 | 中药材拉丁名 | 性 | 味 | 归经 |
| 蔓荆子 | Vitex trifolia L. var. simplicifolia Cham., Vitex trifolia L. | 微寒 | 辛, 苦 | 膀胱, 肝, 胃 |
| 中成药名称 | 处方组成 | 主治疾病 | 中成药类型 |
| 芎菊上清丸 | 川芎,菊花,黄芩,栀子,蔓荆子,黄连,薄荷,连翘,荆芥穗,羌活,藁本,桔梗,防风,甘草,白芷 | 口服,一次6g,一日2次。 | 解表药 |
| 加味感冒丸(感冒丹) | 淡豆鼓,桔梗,忍冬藤,金银花,蔓荆子,蝉蜕,赤小豆,佩兰,栀子,枳壳,连翘,白芷,苦杏仁,天花粉,陈皮,淡竹叶,芦根,荆芥穗,薄荷,赤芍,石膏,甘草,白茅根,防风,黄芩,菊花,桑叶,紫菀,紫苏子,青蒿,莱菔子,化橘红,六神曲,马齿苋,牛蒡子,板蓝根,苍耳子,麻黄,桑白皮,僵蚕,蓼大青叶 | N/A | 解表药 |
| 川芎清脑颗粒 | 川芎,当归,防风,白芷,麦冬,细辛,羌活,独活,苍术,菊花,蔓荆子,黄芩,甘草,生姜 | 开水冲服。一次1袋,一日3次。 | 治风药 |
| 芎菊上清片 | 川芎,菊花,薄荷,连翘,蔓荆子,荆芥穗,防风,白芷,羌活,藁木,桔梗,黄连,黄芩,栀子,甘草 | 口服,一次4片,一日2次。 | 解表药 |
| 黄连上清片 | 黄连,大黄,连翘,薄荷,旋覆花,黄芩,荆芥穗,栀子,防风,石膏,桔梗,黄柏,蔓荆子,白芷,甘草,川芎,菊花 | 口服,一次6片,一日2次。 | 清热药 |
| 清脑复神液 | 人参,黄芪,当归,鹿茸,菊花,薄荷,柴胡,决明子,荆芥穗,丹参,远志,五味子,枣仁,莲子心,麦冬,百合,竹茹,黄芩,桔梗,陈皮,茯苓,甘草,半夏,枳壳,干姜,石膏,冰片,大黄,木通,黄柏,柏子仁,莲子,知母,石菖蒲,川芎,赤芍,桃仁,红花,山楂,牛膝,白芷,藁本,蔓荆子,葛根,防风,羌活,钩藤,地黄 | 口服,轻症一次10ml,重症一次20ml,一日2 次。 | 安神药 |
| 益气聪明丸 | 升麻,葛根,黄柏,白芍,蔓荆子,党参,黄芪,炙甘草 | 口服,一次9g,一日1次。 | 理气药 |
| 换骨丸 | 麻黄,铁丝威灵仙,防风,苍术,蔓荆子,白芷,川芎,桑白皮,苦参,槐角,制何首乌,人参,五味子,木香 | 温黄酒或温开水送服,一次 1丸,一日 2次。 | 表里双解药 |
| 芎菊上清颗粒 | 川芎,菊花,黄芩,白芷,桔梗,栀子,连翘,防风,蔓荆子,荆芥穗,黄连,甘草,羌活,薄荷,藁本 | 开水冲服,一次10g,一日3次。 | 解表药 |
| 辛芳鼻炎胶囊 | 辛夷,白芷,黄芩,柴胡,川芎,桔梗,薄荷,菊花,荆芥穗,枳壳,防风,细辛,蔓荆子,龙胆,水牛角 | 口服,一次6粒,一日2~3次 。 | 清热药 |
| 明目蒺藜丸 | 黄连,川芎,白芷,蒺藜,地黄,荆芥,旋覆花,菊花,薄荷,蔓荆子,黄柏,连翘,密蒙花,防风,赤芍,栀子,当归,甘草,决明子,黄芩,蝉蜕,石决明,木贼 | 口服,一次9克,一日2次。 | 清热药 |
| 罗浮山百草油 | 两面针,徐长卿,九里香,辛夷花,红花,水芙蓉,还魂草,三七,千里光,大头陈,当归,鹅不食草,三七,肿节风,鸡骨香,砂仁,独活,羌活,生姜,陈皮,香附,野菊花,山白芷,桂枝,小罗伞,蔓荆子,桔梗,紫珠叶,地胆草,细辛,五指柑,肉豆蔻,木防己,三叉苦,金银花,救必应,白半枫荷,山苍子,麻黄,地念,防风,半枝莲,铁包金,柴胡,飞天禽劳,鸡骨草,荆芥,虎杖,钩藤,一枝黄花,白花灯笼,白花蛇舌草,人字草,金线风,石仙桃,五月艾,皂角刺,木香,山芝麻,益母草,紫苏叶,倒扣草,侧柏叶,金耳环,一朵云,七叶一枝花,鱼腥草 | 外用,涂搽患处。 | 解表药 |
| 妇科养坤丸 | 熟地黄,甘草,地黄,川芎,当归,延胡索,黄芩,郁金,木香,杜仲,香附,白芍,蔓荆子,砂仁 | 口服,一次1丸,一日2次。 | 补益药 |
| 拨云退翳丸 | 密蒙花,蒺藜(盐炒),菊花,木贼,蝉蜕,荆芥穗,蔓荆子,薄荷,当归,川芎,黄连,甘草 | 口服,一次1丸,一日2次。 | 清热药 |
| 跌打万花油 | 野菊花,乌药,水翁花,徐长卿,大蒜,马齿苋,葱,金银花叶,黑老虎,威灵仙,木棉皮,土细辛,葛花,声色草,伸筋藤,蛇床子,铁包金,倒扣草,苏木,大黄,山白芷,朱砂根,过塘蛇,九节茶,地耳草,一点红,两面针,泽兰,红花,谷精草,土三七,木棉花,鸭脚艾,防风,侧柏叶,马钱子,大风艾,腊梅花,墨旱莲,九层塔,柳枝,栀子,蓖麻子,三棱,辣蓼,莪术,大枫子,荷叶,卷柏,蔓荆子,大皂角,白芷,骨碎补,桃仁,牡丹皮,川芎,化橘红,青皮,陈皮,白及,黄连,赤芍,蒲黄,苍耳子,天南星,紫草茸,胡椒,香附,肉豆蔻,砂仁,紫草, | 外用,擦敷患处。 | 和血药 |
| 五芝地仙金髓膏 | 人参,白术,茯苓,菊花,枸杞子,地黄,麦冬,陈皮,葛根,蔓荆子,六神曲 | N/A | 补益药 |
| 京制牛黄解毒片 | 黄连,黄柏,石膏,金钱花,薄荷,桔梗,连翘,大黄,黄芩,栀子,菊花,荆芥穗,防风,旋复花,白芷,川芎,蔓荆子,蚕砂,甘草,牛黄,冰片 | 口服,一次2片,一日2次。 | 清热药 |
| 天菊脑安胶囊 | 川芎,天麻,菊花,蔓荆子,藁本,白芍,丹参,墨旱莲,女贞子,牛膝 | 口服。每次5粒,一日3次。 | 祛瘀药 |
| 黄连上清丸 | 黄连,栀子,连翘,蔓荆子,防风,荆芥穗,白芷,黄芩,菊花,薄荷,大黄,黄柏,桔梗,川芎,石膏,旋覆花,甘草 | 口服,每10丸重0.3克:一次3克;每10丸重0.6克:一次8克,一日2次。 | 清热药 |
| 健脑益气片 | 黄芪,葛根,川穹,山楂,菊花,蔓荆子,白芷,黄柏 | 口服,一次6片,一日3次。 | 安神药 |
| 方剂名称 | 处方组成 | 剂型 | 处方来源 |
| 升阳补气汤 | 防风,羌活,柴胡,甘草,蔓荆子,升麻,葛根,独活,黄芪,人参,当归,陈皮,黄柏,生地黄,地骨皮 | 汤剂 | 《普济方》卷三九一。 |
| 天门冬煎丸 | 天冬,地骨皮,酥,生地黄,鹿髓,牛髓,桂枝,白术,葳蕤,石菖蒲,远志,泽泻,山药,人参,石斛,牛膝,杜仲,细辛,蔓荆子,独活,枳壳,川芎,黄芪,肉苁蓉,续断,狗脊,萆薢,白芷,巴戟天,刺五加,覆盆子,陈皮,胡麻子,大豆黄卷,茯苓,甘草,石楠叶,柏子仁,川椒,阿胶,鹿角,大枣,薏苡仁 | 丸剂 | 《圣济总录》卷八十四。 |
| 升阳散火汤 | 川芎,蔓荆子,白芍,防风,羌活,独活,甘草,人参,柴胡,香附,葛根,升麻,白僵蚕 | 汤剂 | 《金鉴》卷六十三。 |
| 升清固外汤 | 黄芪,人参,炙甘草,白术,陈皮,当归,白芍,柴胡,蔓荆子,川芎,天花粉 | 汤剂 | 《辨证录》卷二。 |
| 天麻丸48 | 天麻,海蛤壳,白附子,天南星,全蝎,朱砂,白僵蚕,桂枝,羌活,蔓荆子,白花蛇,麻黄,麝香 | 丸剂 | 《圣济总录》卷八十三。 |
| 天麻散35 | 天麻,白花蛇,槐角,羌活,防风,蔓荆子,白鲜皮,蚕沙,枳壳,威灵仙,甘草 | 散剂 | 《圣济总录》卷十二。 |
| 天麻退翳散 | 当归,熟地黄,川芎,赤芍,白僵蚕,蝉蜕,羌活,防风,荆芥,木贼,石决明,白蒺藜,白芷,甘草,麦冬,黄芩,羊角天麻,枳壳,蔓荆子,菊花,蜜蒙花 | 散剂 | 《银海精微》卷下。 |
| 升麻散84 | 细辛,黄柏,知母,防己,黄连,升麻,白芷,蔓荆子,牛蒡子,薄荷 | 散剂 | 《准绳·类方》卷八。 |
| 升阳除湿汤4 | 当归,独活,蔓荆子,防风,炙甘草,升麻,藁本,柴胡,羌活,苍术,黄芪 | 汤剂 | 《兰室秘藏》卷中。 |
| 升麻散50 | 升麻,山茱萸,甘菊,细辛,蔓荆子,山药,防风 | 散剂 | 《圣济总录》卷一一○。 |
| 升阳汤 | 人参,蔓荆子,半夏,黄芪,白术,甘草,白芍,川芎,升麻,白芷 | 汤剂 | 《辨证录》卷二。 |
| 天麻丸38 | 天麻,川芎,天南星,附子,乌梢蛇,桑螵蛸,槐胶,桃胶,酸枣仁,麝香,当归,全蝎,独活,蔓荆子,朱砂 | 丸剂 | 《圣惠》卷三。 |
| 天麻丸47 | 天麻,桂枝,白僵蚕,白附子,朱砂,麝香,犀牛角,蔓荆子,独活,干姜,附子,茯神 | 丸剂 | 《圣惠》卷三。 |
| 内消散13 | 何首乌,玄参,苦参,蔓荆子,威灵仙,甘草,赤小豆 | 散剂 | 《普济方》卷二八八。 |
| 双解散5 | 升麻,葛根,甘草,荆芥,蔓荆子,薄荷,天麻,白僵蚕,知母,贝母 | 散剂 | 《普济方》卷一四七引《经验良方》。 |
| 天麻散18 | 天麻,当归,防风,独活,麻黄,桂心,细辛,附子,蔓荆子 | 散剂 | 《圣惠》卷十九。 |
| 升麻胃风汤 | 升麻,白芷,当归,葛根,苍术,甘草,柴胡,藁本,羌活,黄柏,草豆蔻,麻黄,蔓荆子 | 汤剂 | 《医学入门》卷七。 |
| 天竺黄丸1 | 天竺黄,黄连,柴胡,羚羊角,蔓荆子,犀牛角,防风,黄芩,升麻,麦冬,甘草,玄参,白蒺藜,朱砂,木香,冰片,麝香,牛黄 | 丸剂 | 《圣惠》卷八十三。 |
| 天竺黄丸8 | 当归,川芎,白芷,人参,茯苓,麦冬,防风,荆芥,薄荷,苍耳子,香附,蔓荆子,秦艽,甘草,天竺黄 | 丸剂 | 《古今医鉴》卷九。 |
| 内消散8 | 何首乌,玄参,苦参,蔓荆子,威灵仙 | 散剂 | 《卫济宝书》卷下。 |
对于不同动物的给药剂量换算,您也可以参考 更多...
请在以下方框中输入您的动物实验信息后点击计算,可以得到母液配置方法和体内配方的制备方法: 比如您的给药剂量是10 mg/kg,每只动物体重20 g,给药体积100 μL,一共给药动物10 只,您使用的配方为5% DMSO+30% PEG300+5% Tween 80+60% ddH2O。那么您的工作液浓度为2 mg/mL。
母液配置方法:2 mg 药物溶于 50 μL DMSO (母液浓度为 40 mg/mL), 如您需要配置的浓度超过该产品的溶解度,请先与我们联系。
体内配方的制备方法:取 50 μL DMSO 主液,加入 300 μL PEG300, 混匀澄清,再加 50 μL Tween 80,混匀澄清,再加 600 μL ddH2O, 混匀澄清。
您可能有的问题的答案可以在抑制剂处理说明中找到,包括如何准备库存溶液,如何存储产品,以及基于细胞的分析和动物实验需要特别注意的问题。
Chrysosplenol D 14965-20-9 Immunology/Inflammation MAPK NF-Κb IL Receptor NF-κB JNK cancer Apoptosis inhibit ERK1/2 Inhibitor antitrypanosomal breast anti-inflammatory 猫眼草酚D inhibitor
